- Goodfellas
- The King of Comedy
- Taxi Driver
- Casino
- Mean Streets
- Raging Bull
- After Hours
- The Last Temptation of Christ
- Shutter Island
- Gangs of New York
- The Age of Innocence
- Cape Fear
- Bringing Out the Dead
- Kundun
- The Departed
- The Aviator
- The Color of Money
Month: May 2013
Required Reading — Carl Larsson

“What past consecutive causes, before rising preapprehended, of accumulated fatigue did Bloom, before rising, silently recapitulate?” (Ulysses)
What past consecutive causes, before rising preapprehended, of accumulated fatigue did Bloom, before rising, silently recapitulate?
The preparation of breakfast (burnt offering): intestinal congestion and premeditative defecation (holy of holies): the bath (rite of John): the funeral (rite of Samuel): the advertisement of Alexander Keyes (Urim and Thummim): the unsubstantial lunch (rite of Melchisedek): the visit to museum and national library (holy place): the bookhunt along Bedford row, Merchants’ Arch, Wellington Quay (Simchath Torah): the music in the Ormond Hotel (Shira Shirim): the altercation with a truculent troglodyte in Bernard Kiernan’s premises (holocaust): a blank period of time including a cardrive, a visit to a house of mourning, a leavetaking (wilderness): the eroticism produced by feminine exhibitionism (rite of Onan): the prolonged delivery of Mrs Mina Purefoy (heave offering): the visit to the disorderly house of Mrs Bella Cohen, 82 Tyrone street, lower and subsequent brawl and chance medley in Beaver street (Armageddon)—nocturnal perambulation to and from the cabman’s shelter, Butt Bridge (atonement).
A summary of sort of Bloom’s day. From the penultimate chapter of James Joyce’s Ulysses.
Silver Surfer — Jack Kirby
“Prayer to Persephone” — Edna St. Vincent Millay

Žižek Tells a Dirty Joke
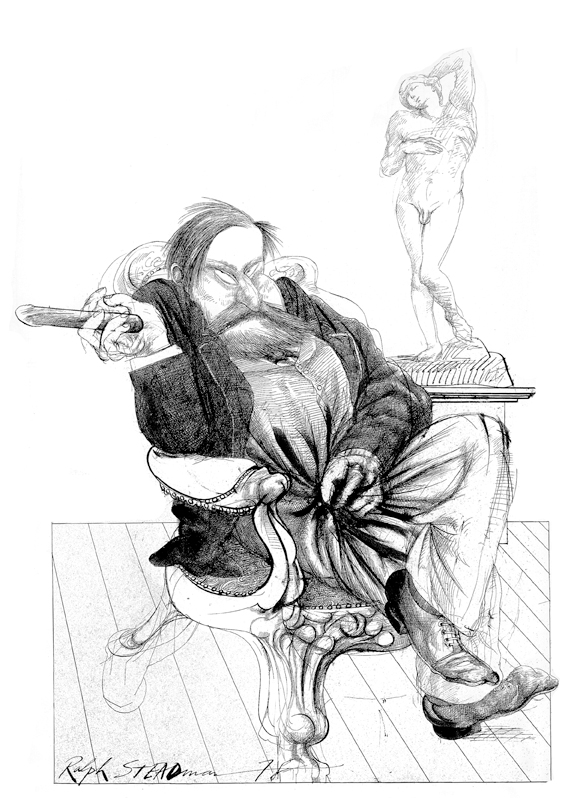
Portrait of Sigmund Freud — Ralph Steadman

Alan Furst Novel (Book Acquired, 5.22.2013)

Alan Furst’s Mission to Paris is new in trade paperback this month. Publisher Random House’s blurb:
Late summer, 1938. Hollywood film star Fredric Stahl is on his way to Paris to make a movie. The Nazis know he’s coming—a secret bureau within the Reich has been waging political warfare against France, and for their purposes, Fredric Stahl is a perfect agent of influence. What they don’t know is that Stahl, horrified by the Nazi war on Jews and intellectuals, has become part of an informal spy service run out of the American embassy. Mission to Paris is filled with heart-stopping tension, beautifully drawn scenes of romance, and extraordinarily alive characters: foreign assassins; a glamorous Russian actress-turned-spy; and the women in Stahl’s life. At the center of the novel is the city of Paris—its bistros, hotels grand and anonymous, and the Parisians, living every night as though it were their last. Alan Furst brings to life both a dark time in history and the passion of the human hearts that fought to survive it.
“On the Art of Fiction” — Willa Cather
“On the Art of Fiction” by Willa Cather
One is sometimes asked about the “obstacles” that confront young writers who are trying to do good work. I should say the greatest obstacles that writers today have to get over, are the dazzling journalistic successes of twenty years ago, stories that surprised and delighted by their sharp photographic detail and that were really nothing more than lively pieces of reporting. The whole aim of that school of writing was novelty—never a very important thing in art. They gave us, altogether, poor standards—taught us to multiply our ideas instead of to condense them. They tried to make a story out of every theme that occurred to them and to get returns on every situation that suggested itself. They got returns, of a kind. But their work, when one looks back on it, now that the novelty upon which they counted so much is gone, is journalistic and thin. The especial merit of a good reportorial story is that it shall be intensely interesting and pertinent today and shall have lost its point by tomorrow.
Art, it seems to me, should simplify. That, indeed, is very nearly the whole of the higher artistic process; finding what conventions of form and what detail one can do without and yet preserve the spirit of the whole—so that all that one has suppressed and cut away is there to the reader’s consciousness as much as if it were in type on the page. Millet had done hundreds of sketches of peasants sowing grain, some of them very complicated and interesting, but when he came to paint the spirit of them all into one picture, “The Sower,” the composition is so simple that it seems inevitable. All the discarded sketches that went before made the picture what it finally became, and the process was all the time one of simplifying, of sacrificing many conceptions good in themselves for one that was better and more universal.
Any first rate novel or story must have in it the strength of a dozen fairly good stories that have been sacrificed to it. A good workman can’t be a cheap workman; he can’t be stingy about wasting material, and he cannot compromise. Writing ought either to be the manufacture of stories for which there is a market demand—a business as safe and commendable as making soap or breakfast foods—or it should be an art, which is always a search for something for which there is no market demand, something new and untried, where the values are intrinsic and have nothing to do with standardized values. The courage to go on without compromise does not come to a writer all at once—nor, for that matter, does the ability. Both are phases of natural development. In the beginning the artist, like his public, is wedded to old forms, old ideals, and his vision is blurred by the memory of old delights he would like to recapture.
The Borzoi, 1920
Reading the Part — Pierre-Auguste Renoir

F. Scott Fitzgerald’s Handwritten Manuscript for the First Page of Gatsby
Andy Warhol Shills for Pioneer Audio

Molly’s Suitors (Ulysses)
If he had smiled why would he have smiled?
To reflect that each one who enters imagines himself to be the first to enter whereas he is always the last term of a preceding series even if the first term of a succeeding one, each imagining himself to be first, last, only and alone whereas he is neither first nor last nor only nor alone in a series originating in and repeated to infinity.
What preceding series?
Assuming Mulvey to be the first term of his series, Penrose, Bartell d’Arcy, professor Goodwin, Julius Mastiansky, John Henry Menton, Father Bernard Corrigan, a farmer at the Royal Dublin Society’s Horse Show, Maggot O’Reilly, Matthew Dillon, Valentine Blake Dillon (Lord Mayor of Dublin), Christopher Callinan, Lenehan, an Italian organgrinder, an unknown gentleman in the Gaiety Theatre, Benjamin Dollard, Simon Dedalus, Andrew (Pisser) Burke, Joseph Cuffe, Wisdom Hely, Alderman John Hooper, Dr Francis Brady, Father Sebastian of Mount Argus, a bootblack at the General Post Office, Hugh E. (Blazes) Boylan and so each and so on to no last term.
A passage from the penultimate episode of James Joyce’s Ulysses.
Study for Portrait II (after the Life Mask of William Blake) — Francis Bacon

Lydia Davis Reads “The Cows”
“The Shrinkage of the Planet” — Jack London
“The Shrinkage of the Planet” by Jack London
What a tremendous affair it was, the world of Homer, with its indeterminate boundaries, vast regions, and immeasurable distances. The Mediterranean and the Euxine were illimitable stretches of ocean waste over which years could be spent in endless wandering. On their mysterious shores were the improbable homes of impossible peoples. The Great Sea, the Broad Sea, the Boundless Sea; the Ethiopians, “dwelling far away, the most distant of men,” and the Cimmerians, “covered with darkness and cloud,” where “baleful night is spread over timid mortals.” Phœnicia was a sore journey, Egypt simply unattainable, while the Pillars of Hercules marked the extreme edge of the universe. Ulysses was nine days in sailing from Ismarus the city of the Ciconians, to the country of the Lotus-eaters—a period of time which to-day would breed anxiety in the hearts of the underwriters should it be occupied by the slowest tramp steamer in traversing the Mediterranean and Black Seas from Gibraltar to Sebastopol.
Homer’s world, restricted to less than a drummer’s circuit, was nevertheless immense, surrounded by a thin veneer of universe—the Stream of Ocean. But how it has shrunk! To-day, precisely charted, weighed, and measured, a thousand times larger than the world of Homer, it is become a tiny speck, gyrating to immutable law through a universe the bounds of which have been pushed incalculably back. The light of Algol shines upon it—a light which travels at one hundred and ninety thousand miles per second, yet requires forty-seven years to reach its destination. And the denizens of this puny ball have come to know that Algol possesses an invisible companion, three and a quarter millions of miles away, and that the twain move in their respective orbits at rates of fifty-five and twenty-six miles per second. They also know that beyond it are great chasms of space, innumerable worlds, and vast star systems.
While much of the shrinkage to which the planet has been subjected is due to the increased knowledge of mathematics and physics, an equal, if not greater, portion may be ascribed to the perfection of the means of locomotion and communication. The enlargement of stellar space, demonstrating with stunning force the insignificance of the earth, has been negative in its effect; but the quickening of travel and intercourse, by making the earth’s parts accessible and knitting them together, has been positive.
The advantage of the animal over the vegetable kingdom is obvious. The cabbage, should its environment tend to become worse, must live it out, or die; the rabbit may move on in quest of a better. But, after all, the swift-footed creatures are circumscribed in their wanderings. The first large river almost inevitably bars their way, and certainly the first salt sea becomes an impassable obstacle. Better locomotion may be classed as one of the prime aims of the old natural selection; for in that primordial day the race was to the swift as surely as the battle to the strong. But man, already pre-eminent in the common domain because of other faculties, was not content with the one form of locomotion afforded by his lower limbs. He swam in the sea, and, still better, becoming aware of the buoyant virtues of wood, learned to navigate its surface. Likewise, from among the land animals he chose the more likely to bear him and his burdens. The next step was the domestication of these useful aids. Here, in its organic significance, natural selection ceased to concern itself with locomotion. Man had displayed his impatience at her tedious methods and his own superiority in the hastening of affairs. Thenceforth he must depend upon himself, and faster-swimming or faster-running men ceased to be bred. The one, half-amphibian, breasting the water with muscular arms, could not hope to overtake or escape an enemy who propelled a fire-hollowed tree trunk by means of a wooden paddle; nor could the other, trusting to his own nimbleness, compete with a foe who careered wildly across the plain on the back of a half-broken stallion. Continue reading ““The Shrinkage of the Planet” — Jack London”
Reading — Nikolaos Lytras


